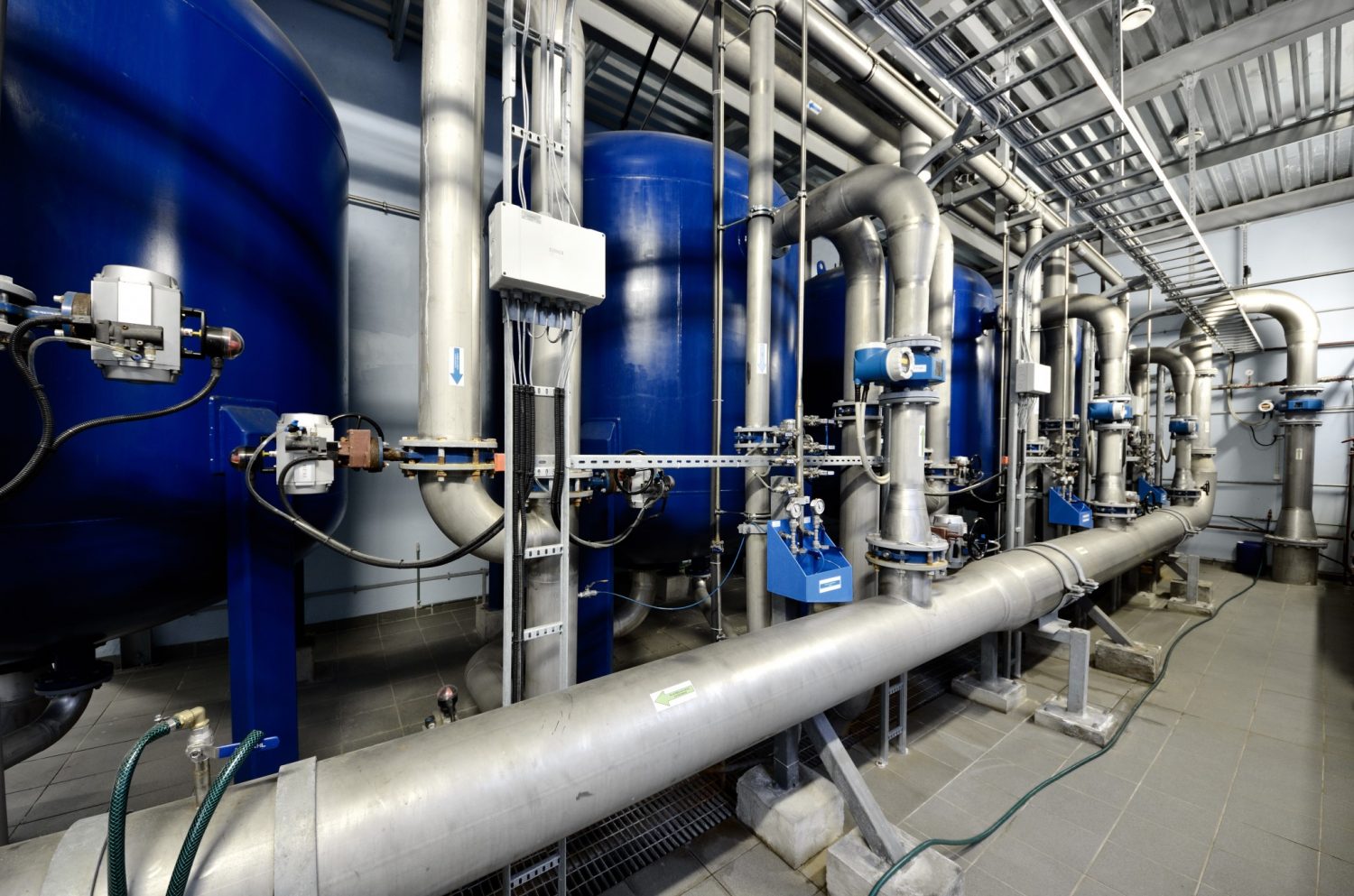
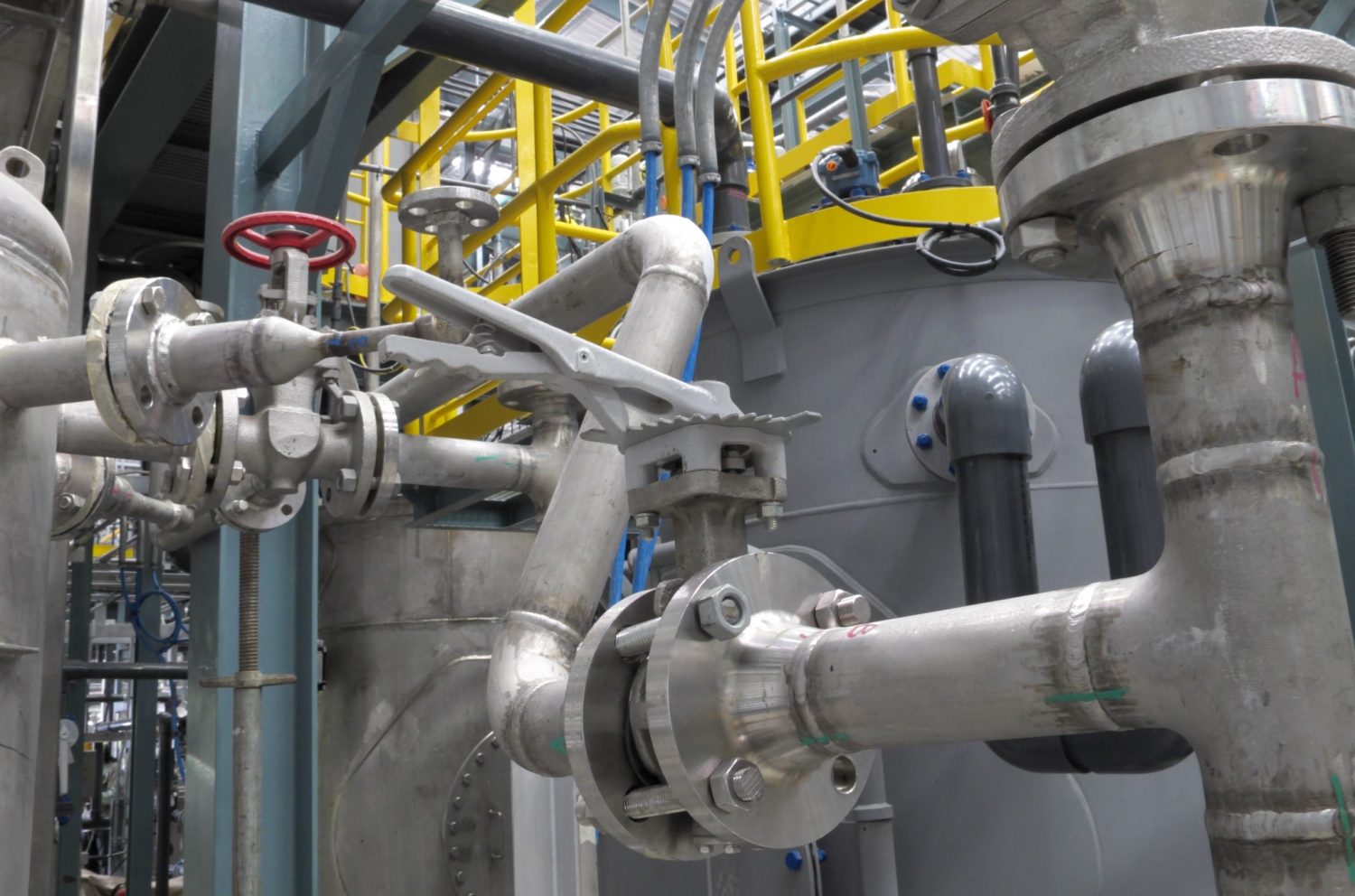
Why Choose Aero-Flex For your ASME Piping Assemblies?
ASME B31 Power Piping Systems
ASME Power Piping and Process Piping play pivotal roles across diverse industries. This ensures the safe and efficient transportation of fluids under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Additionally, ASME has established standards and codes to govern the design, construction, and maintenance of power piping systems.
Aero-Flex Corp. specializes in fabricating simple and complex ASME-certified power piping and process piping spools. Our expertise extends to a wide range of pipe sizes, ranging from 1/4″ to 14″ in diameter, and varying wall thicknesses. Typically from schedule 10 to schedule 160 in thickness. To ensure the highest quality, each weld is meticulously inspected during the fabrication process. Its inspected again during final QC inspection, led by our Certified Welding Inspector (CWI).
In addition to our rigorous quality control measures, Aero-Flex Corp. offers Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) services. This includes radiographic inspection (X-Ray), liquid penetrant inspection, and magnetic particle inspection. Moreover, we provide the option of standard or high purity cleaning for any of the assemblies we build.
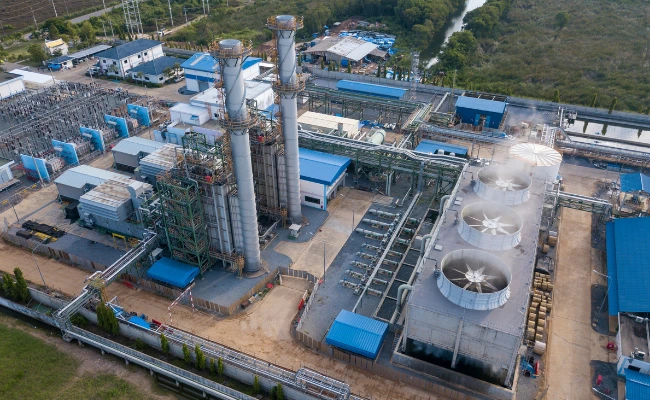

What is ASME B31 Power Piping?
Understanding ASME B31 Power Piping
ASME B31 Power Piping is a widely recognized standard governing the design, fabrication, installation, inspection, and maintenance of power piping systems. Encompassing materials, design factors, pressure ratings, testing, and safety considerations. The code applies to piping systems in power plants, refineries, chemical plants, and industrial facilities handling high-pressure and high-temperature fluids.
Importance Of ASME B31 Power Piping:
The ASME B31 Power Piping standard ensures the integrity and reliability of power piping systems. Minimizing the risk of failures, leaks, and accidents. This commitment to compliance enhances safety for personnel and protects the environment. Additionally, adherence to ASME B31 helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry best practices. This provides a framework for consistent and efficient piping system operations.
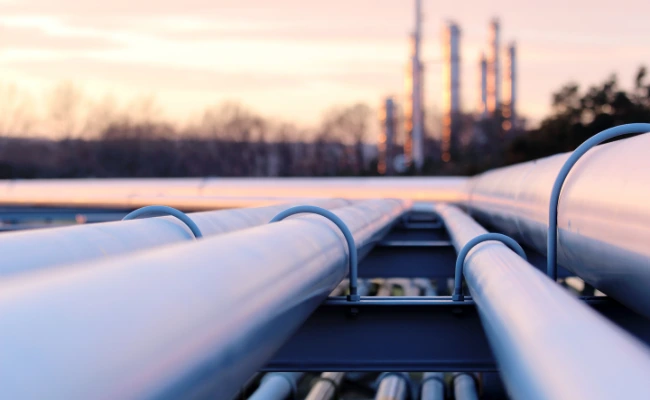

With extensive experience in fabricating custom process piping and power piping spools, Aero-Flex specializes in complete piping systems. Our high-quality piping systems and assemblies can be found in some of the world’s largest oil and gas and power turbine companies, including GE Power, GE Oil & Gas, and Pratt & Whitney Power Systems. Throughout the fabrication process, our Certified Weld Inspector (CWI) ensures that all welds meet specifications, and every assembly undergoes a final accuracy and quality check before shipment to our customers.
To maintain stringent quality standards, Aero-Flex has a certified Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) expert on staff for penetrant inspections, and we operate a certified NDT lab for radiograph (X-Ray) inspections when necessary. Our commitment to precision and quality control ensures reliable and safe piping solutions for our valued customers.
Key Elements Of ASME B31 Power Piping
Materials Selection
The selection of suitable materials is crucial for power piping systems. ASME B31 provides guidance on the materials to be used based on factors such as pressure, temperature, and fluid properties. Additionally, the standard specifies acceptable materials for different piping components, ensuring their compatibility with the intended service conditions and minimizing the risk of corrosion, erosion, and other forms of degradation. To ensure the correct material is used, Aero-Flex verifies the specification and alloy on the Material Test Report received from our material supplier. It is a mandatory requirement for all Aero-Flex material purchases to come with material test reports and a manufacturer certificate of conformance. This meticulous approach guarantees reliable and compliant material usage in our piping solutions.
Design Factors
ASME B31 outlines design considerations for power piping systems, encompassing factors such as pressure, temperature, loadings, supports, and flexibility. These crucial factors play a significant role in determining the structural integrity, reliability, and overall performance of the piping system. Through meticulous design calculations and engineering analysis, the appropriate pipe size, wall thickness, and support requirements are determined, ensuring the system can withstand the demanding operating conditions and external forces. This comprehensive approach guarantees the safety and efficiency of the power piping systems.
Pressure Ratings
The standard provides comprehensive guidelines for determining the pressure ratings of power piping components. It takes into account factors such as material strength, design pressure, temperature, and safety margins to establish the maximum allowable pressure that the piping system can safely withstand. To ensure the integrity of the installed piping, ASME B31 also outlines pressure testing and inspection procedures. This meticulous approach guarantees the safe and reliable operation of the power piping system under varying pressure conditions.
Testing and Inspection
ASME B31 places significant emphasis on testing and inspection throughout the entire life cycle of power piping systems. The standard defines comprehensive procedures for various tests, including hydrostatic testing, leak testing, non-destructive examination, and visual inspection. These rigorous tests play a crucial role in ensuring the quality, performance, and utmost safety of the piping. By conducting these tests, potential defects or failures can be detected early on, facilitating prompt corrective measures and enhancing the overall reliability of the power piping system.
The Aero-Flex Touch
Our meticulous approach to fabricating piping assemblies sets us apart. Each welded assembly undergoes rigorous hydrostatic or pneumatic pressure testing, ensuring its structural integrity and reliability. But it doesn’t end there – we go the extra mile to guarantee the highest quality by conducting thorough internal and external cleaning.
Additionally, Our cleaning process involves the application of a potent degreaser and etching acid, effectively eliminating any residues or contaminants from the pipe while also cleaning it. Additionally, we use a specialized pickling acid on the welds, extracting carbon and other impurities, leaving them pristine. We don’t stop until the welds are scrubbed diligently, resulting in welds that remain impervious to rust or deterioration for many years to come.


At Aero-Flex, we take great pride in delivering exceptional results through our pickling process. It’s this level of dedication and attention to detail that ensures our piping assemblies are not only safe and reliable but also of the highest quality. When it comes to fabricating your process piping or power piping spools, you can’t entrust the task to just anyone. Our team boasts an impressive 75 years of experience in metal fabrication and welding, coupled with a comprehensive understanding of the specifications necessary to deliver a process piping system that surpasses your expectations.
To see some examples of some of our piping projects please go to our gallery page.
Also see our CNC machining services and high temperature air and steam hoses.



